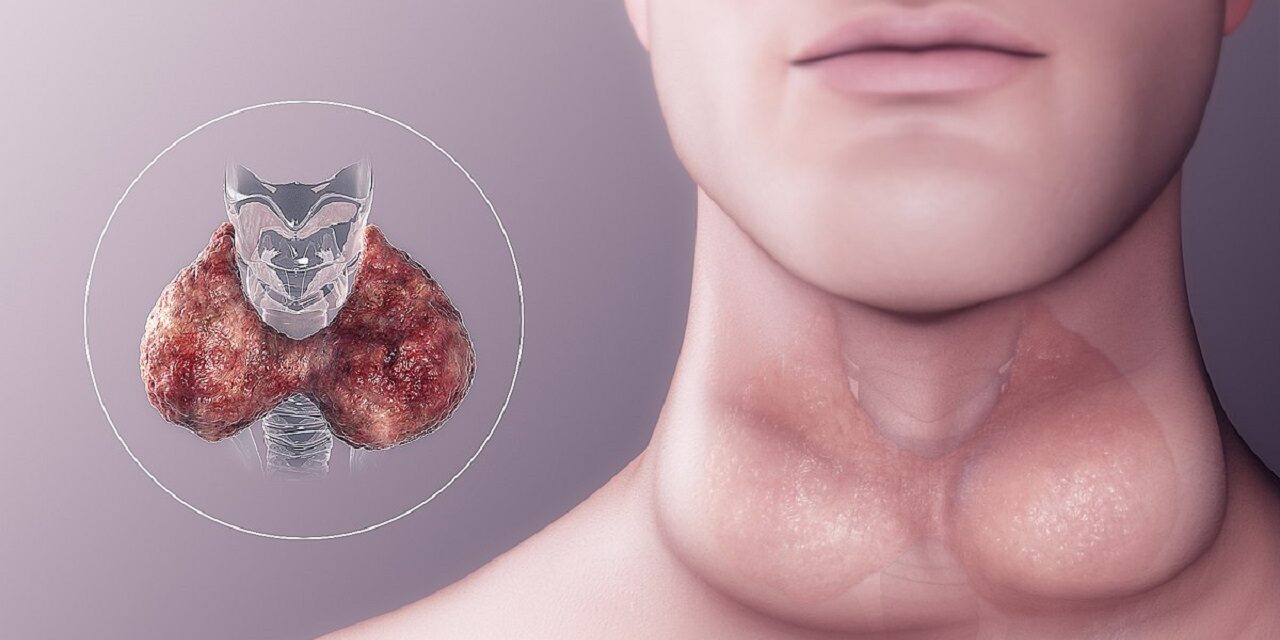
Hypothyroidism Explained: What You Need to Know
Have you ever felt unusually tired, gained weight without any real explanation, or noticed your skin turning rough and dry? Many people blame these changes on aging or stress, but the truth could lie deeper — inside a small, butterfly-shaped gland in your neck known as the thyroid. When this gland slows down and fails to produce enough hormones, the condition is called hypothyroidism.
The Silent Controller of Your Body
The thyroid gland is a small organ, but its job is massive. It produces hormones that guide your body’s metabolism, which determines how your body uses energy. When this process slows down, the entire system — from your heart rate to your digestion and even your mood — can be affected. An underactive thyroid makes everyday life feel slower, more tiring, and harder to manage.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
What makes hypothyroidism especially tricky is that its symptoms often develop so gradually that they’re easy to overlook. People living with it may notice persistent tiredness, unexplained weight gain, and even feeling cold more often than others. Skin can turn dry, hair might thin out, and some even find their memory and focus fading over time. Women may experience irregular menstrual cycles, while others report mood changes or ongoing feelings of sadness. Because the signs are so common, many assume it's just part of a busy life or aging — but in reality, it’s the thyroid asking for help.
What Causes Hypothyroidism to Develop?
There are several reasons why the thyroid gland may slow down. One of the leading causes is an autoimmune condition known as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. In this case, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid, gradually damaging it and lowering hormone production. Hypothyroidism can also occur after thyroid surgery or radiation treatments, often following cancer therapy or when treating thyroid nodules. In some parts of the world, especially in areas where iodine intake is low, iodine deficiency can lead to the condition, since iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. Certain medications can also slow thyroid activity, though not everyone is aware of this risk.
Diagnosis: A Simple Blood Test Can Reveal the Truth
Unlike many health conditions, diagnosing hypothyroidism is fairly straightforward. Doctors typically recommend a blood test to check levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone, or TSH. When thyroid hormone levels are too low, the brain signals the pituitary gland to release more TSH in an effort to stimulate the thyroid. High TSH levels usually indicate an underactive thyroid. Often, a second test will be done to measure T4 hormone levels for confirmation. Identifying hypothyroidism early can help prevent complications like heart disease, infertility, or nerve damage.
Treating Hypothyroidism: A Lifelong but Simple Process
When it comes to treatment, hypothyroidism can usually be managed with medication. Doctors often prescribe levothyroxine, a synthetic hormone that works as a replacement for the thyroid hormones your body is missing. Adjusting the dosage to suit each person’s needs is key, and regular follow-ups ensure that hormone levels stay balanced. Once on the right treatment plan, most people start to notice improvements in their energy, mood, and weight control within a few weeks.
Healthy Habits That Support Thyroid Function
Beyond medication, everyday habits play a powerful role in managing hypothyroidism. Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients — including iodine, selenium, and zinc — can support thyroid health. Seafood, dairy, eggs, and iodized salt are some of the best natural sources. Alongside diet, managing stress is important too, as constant stress can disrupt hormone balance. Gentle activities like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help calm both the mind and body. Regular physical exercise, even simple walking or stretching, can improve metabolism and reduce many of the uncomfortable symptoms linked to hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism in India: A Growing Health Concern
In India, thyroid disorders are more common than many realize, particularly among women. Because the symptoms develop so slowly, hypothyroidism is often mistaken for other issues, leading to delayed diagnosis and long-term discomfort. Raising awareness about this condition can help people seek testing and start treatment sooner, improving quality of life significantly.
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism is a manageable condition, but only if you listen to the signals your body is sending. Feeling tired, gaining weight unexpectedly, or noticing changes in your skin and mood are not always “normal” — sometimes they’re warning signs from your thyroid. Fortunately, with timely diagnosis and proper treatment, people living with hypothyroidism can regain their energy, focus, and balance. A simple blood test could be the first step toward feeling better and taking control of your health.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms or simply want to ensure your thyroid is functioning at its best, visit Jothi Hospital for expert consultation and care. Our team is here to guide you toward better health, one step at a time.